Contents
Howard Sheth Model
Howard Sheth Model is a model on consumer behaviour that was introduced by John Howard and Jagadish Sheth in Year 1969. It is the first integrated model on consumer behaviour developed by utilizing the learning theory in a through and systematic manner by Howard. This model is an attempt to evaluate how the integrated efforts of social, psychological and marketing forces influences the preferences and buying behaviour of consumer into a logical sequence of information processing.
It shows how a consumer responds to the buying decisions over a period of time. The model tells how in case of incomplete information and reducing processing capability, a consumer responds to the choice of products. This concept on consumer behaviour was published in book “The theory of Consumer Behaviour”.
Howard Sheth Model Level of Decision-making
Howard Sheth Model depicted that there are three crucial stages in case of decision making or choice of brand by buyer. These 3 stages are as follows: –
- Extensive Problem Solving
- Limited Problem Solving
- Routinized Response Behaviour
Extensive Problem Solving
Extensive Problem Solving is a starting stage in decision making of buyer. At this stage, consumer is a new comer to market having lack of information regarding products or brands. Consumer has no preference for a particular brand and has not developed any proper criteria for making choice among available products.
Consumer seek to attain more information about market by checking out different varieties of available brands.He aims to collect information about products before making any purchase decision.
Limited Problem Solving
Limited Problem Solving is more advanced stage of buyer decision making as compared to Extensive Problem solving. Buyer has developed well-defined criteria for choosing products but is still confused about choosing brand due to availability of incomplete information. Buyer has inadequate information regarding products and brands operating in market. He is uncertain which brand is right choice for serving him in the best way.
Therefore, for making a certain purchase decision,he goes for a comparative analysis of distinct products and brands existing in market.
Routinized Response Behaviour
Routinized Response Behaviour is a stage where consumer has full information about market and has a well-defined criteria of choice. He is aware of features, pros and cons of different products available. Consumer is in a position of evaluating and doing a comparative analysis of various alternatives present in market. He is well informed about the market conditions and therefor make a decision in advance which product to be purchased or not.
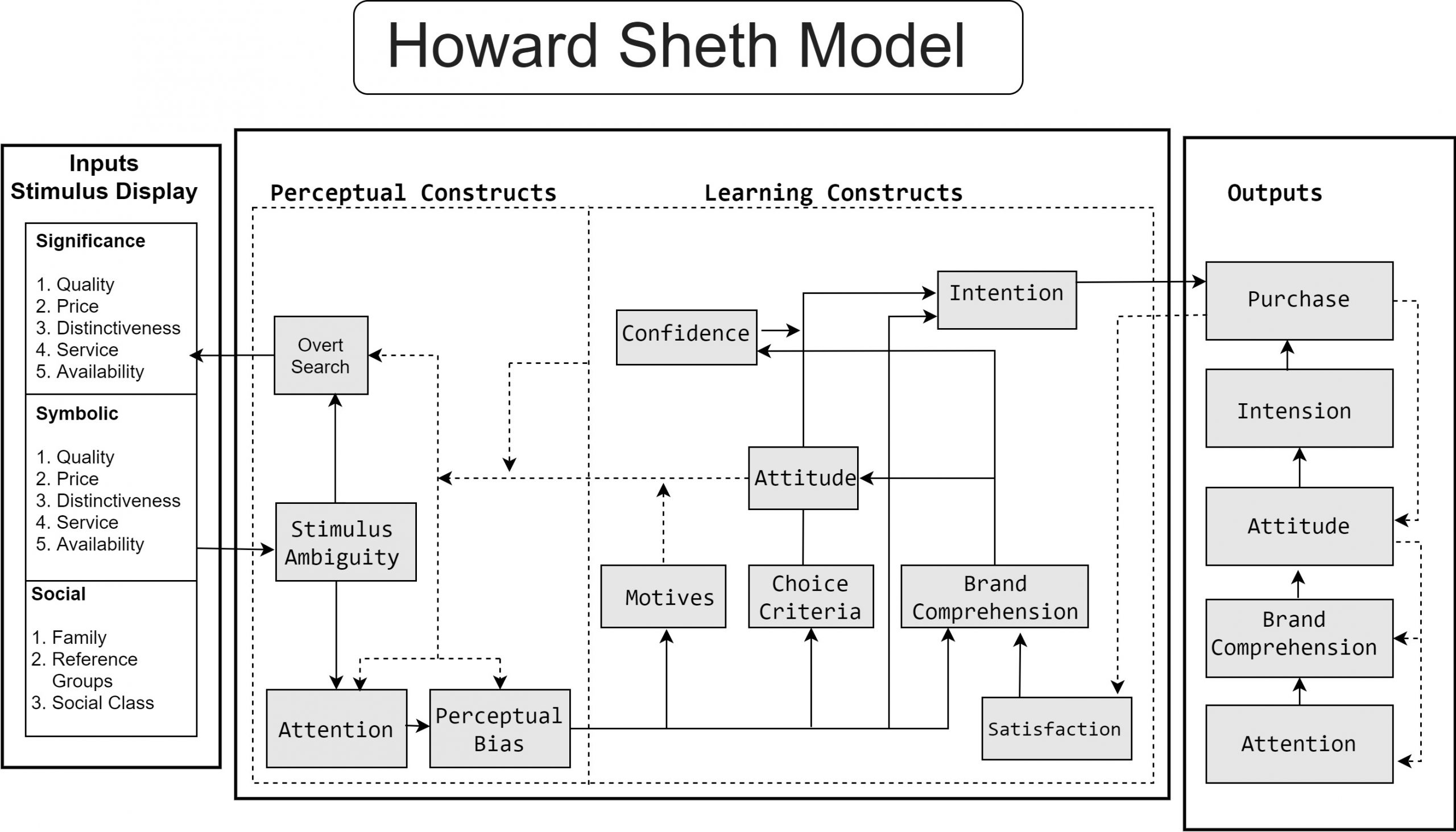
Variables of Howard Sheth Model
Starting with level of Extensive problem solving, the consumer transforms slowly into regular customer of brand, at Routinized Response behaviour level.
Consumer process of decision making wholly works on four main components of this model which can also be termed as 4 pillars of Howard Sheth model.
Elements Of Howard Sheth Model
- Input Variables
- Hypothetical Constructs
- Output variables
- Exogenous variables
Input Variables
Input variables comprises of informational clues regarding the features of product like its quality, price, uniqueness, service and availability. It is a stimulus resulting from marketing activities of brand and social environment of buyer.
It can be further classified into three categories as: –
Significant Stimuli:Significant stimuli refers to the physical attributes and features of a product. It comprises of price of product, its quality, its uniqueness, type of service and accessibility in market.
Symbolic Stimuli:It means the visual features of product that are portrayed by sales people and marketing strategies used by brand. Promotional messages and publicity done by seller develops a psychological impact on consumer’s perception about features of product.
Social Stimuli: Social stimuli includes the social environment of consumers which provide information about market and influence his/her buying decision.It consists of family, reference groups and social class of buyer in general.
Hypothetical constructs
Hypothetical constructs is the one that portray the main portion of Howard Sheth model. It comprises of all such psychological variables that influence the buyer’s behaviour while making purchase decisions.
It can be further categorized into 2 categories: –
Perceptual constructs
Learning constructs
Perceptual constructs: It describes the way in which buyer procure, process and perceive information from input variables. It is a vital component as it influences the selection of brand and finally the purchase by consumer. It includes: –
Sensitivity to information-Buyer’s sensitivity and understanding level towards the message received by him.
Perceptual bias-Partialness of a buyer towards a specific brand on grounds of each brand’s individual perception.
Information search-Buyer for taking proper decisions looks out for attaining more information.
Learning Constructs: Learning constructs relates to buyer’s state of knowledge, attitude, opinion, confidence and final decision on selection of products and brand.
Motive-Motive refers to the ultimate purpose for buying the product.
Choice criteria- Choice criteria is the benchmark which buyer uses for choosing a product or brand.
Brand Comprehension-Buyer’s present state of information regarding the brand pertained by him.
Attitude-Attitude is the willingness of buyer to purchase the brand’s product.
Confidence- Confidence is the outcome of trust that buyer have in a particular brand.
Intention- It is final selection of a specific brand that results from motive of buyer, his preference criteria, attitude and confidence.
Satisfaction-It is the post-purchase benefit derived by buyer from product usage, whether it has fulfilled his/her expectations or not.
Output Variables
It is the outcome of decision making process of buyer that can be seen through his observable response towards input variables. There are five set of output variables that are arranged in order from attention to actual purchase.
These set of output variables arranged in a systematic manner are: –
Attention-Attention is the buyer’s state of alertness for understanding the information provided to him.
Brand Comprehension-Brand comprehension is buyer’s awareness towards the brand and its products.
Attitude-It is the buyer interest and behaviour towards a particular product which is determined by his/her individual likes and dislikes.
Intention-Buyer intention is the main objective or aim for buying a particular product.
Purchase Behaviour-At last, buyer finally buys the product which is the outcome of all above components.
Exogenous Variables
Exogenous variables are other external forces that are notdirectly involved in decision making process of buyer but have a significant impact on his buying decisions.These are the environmental forces which affect purchase behaviour of consumer by hampering the purchase of a product of preferred brand.
These variables are listed below: –
Purchase Importance-It is the degree of importance and value of purchase as perceived by buyer which influence his/her preference for brand.
Personality Variables-These are the personal traits of buyer that influence his decisions while buying a product such as ego, anxiety, self-esteem, authoritarian and dominance.
Culture-Culture refers to values, ideas and beliefs of buyer that make up his/her motive of purchase.
Social class-It is the social group of individual comprising of his family, friend and reference groups that affects the decisions for choosing a particular brand.
Organization-Power, authority and status of individual is defined by their interaction with various social groups. These formal and informal communications of buyer influence his hypothetical constructs.
Time Pressure-It refers to time period when product of a preferred brand is not available in market and buyer is under high pressure to look for various alternatives available and take a timely decision.
Financial Status-It refers to inability of an individual for purchasing a product which restricts him/her from buying it.
Conclusion
This model mainly focuses on repetitive purchase behaviour of individuals or industrial buyers. Howard Sheth model is an empirical approach towards recognizing the mindset of a consumer while making purchase decisions. However, this model lacks reliability because of its dependence on hypothetical constructs.