Contents
Meaning
Strategies designed by a company for pricing its products and services are called Price Policies. Every company has limited flexibility to price its product as it has to provide value as well as pocket-friendly products to its customers and reap profits at the same time. For this, it has to create rational goals and strategize its policies in a way that it can gain dual benefits.
Generally, price policies work in the following ways:
i) If the company is at an early age or in the budding stage, it keeps the price of its product low so that it can make a smooth entry into the market and gain market share.
ii) If the company has created a disrupting product and sees heavy demand for its product, it tends to keep sky-rocketing prices to gain heavy revenue.
Moreover, if the company is operating in a highly competitive market, it keeps its price equal to the average price of that industry so that it is not discarded from the market.
Objectives of Price Policy
Pricing of products is done to meet certain organizational objectives. To list a few:
Capturing Market Share
Nowadays, companies are in the momentum of achieving more and more market share. This is done to eliminate competition and gain goodwill as well as acquire sizable customers. Once they achieve their benchmarked market share, they can easily attain voluminous sales too.
Achieving Substantial Sales and Profit
The basic organizational objective of every company is to survive, make a profit and grow. Thus, they effectively utilize their human and material resources to engage sales and generate revenue.
Beating Competition
Companies look for virality factors in their product i.e, they want their customers to market their products. This way they can convince other customers to drift from their existing products, which is a competition for these companies, and buy their product.
Target Return
Every organization has a target return to achieve at the end of the financial period and assure they have minimum stock at their backlog. Organizations strive hard to increase their ratio of profit to sales.
Profit to sales is a proportional measure of profits generated out of total sales revenue.
Importance of Price Policy
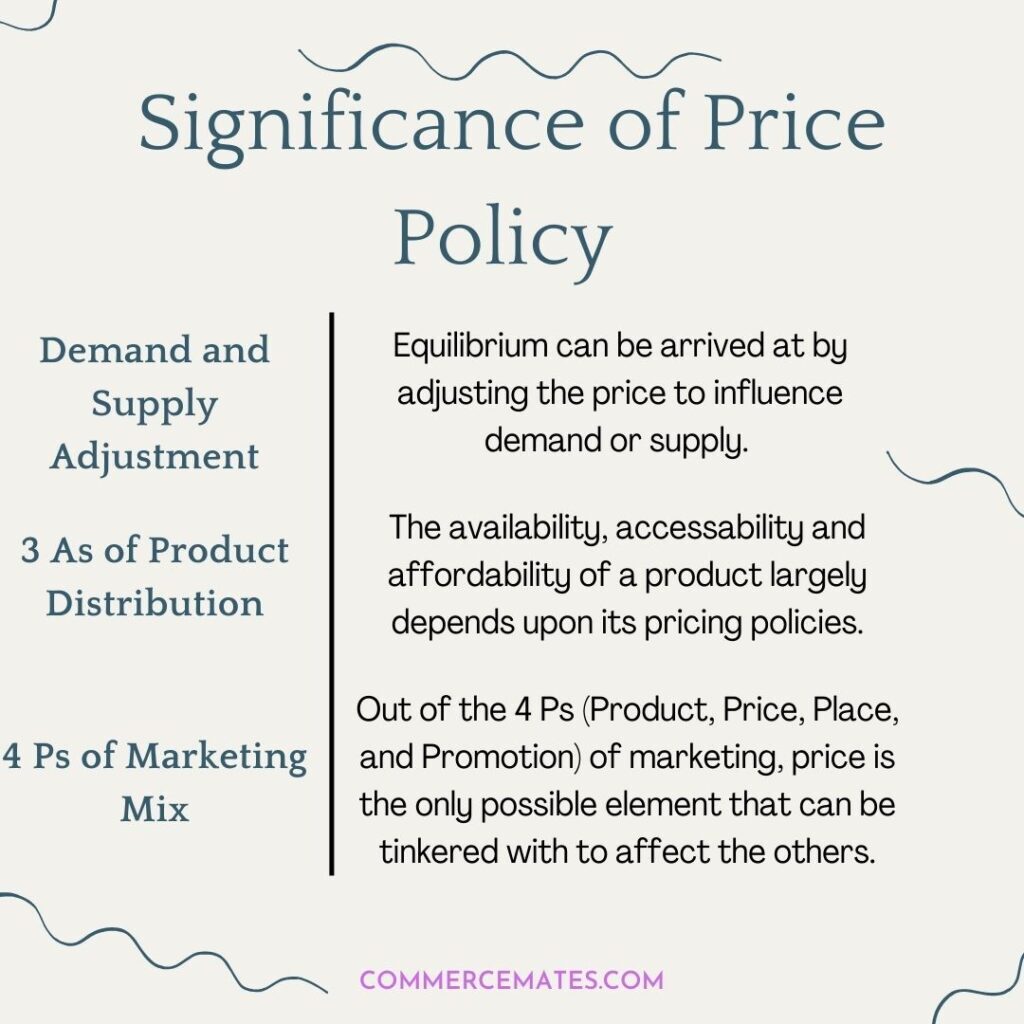
Demand and Supply Adjustment
One of the most important roles played by Price Policy is demand and supply adjustment. If demand for a product is high, its price can be increased to meet the existing supply.
Similarly, if the supply of the product is in bulk, the price can be reduced to encourage its sales and this would drive automatic demand. This way, the company can arrive at equilibrium.
3 ‘A’s of Product Distribution
Price can also be considered the backbone of 3 “As”: Availability, Accessibility, and Affordability.
Rational costing would help producers add their profit margin and make the product available in the market. Cost customized distribution system would make them accessible to various places.
Lastly, price is the first impression of every product. No matter how quality-driven and classy the product is; consumers make sure it lies within their budget. Thus, affordability enters the market here.
4 ‘P’s of Marketing Mix
There are 4Ps of marketing mix: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. Except for the price, every other “P” is constant i.e., it cannot be changed.
For example, the producer is bound to manufacture raincoats during the rainy season and sell them in those areas where the monsoon is yet to arrive. He cannot customize a place or product according to his cost. However, he can adjust the price concerning raw material consumption and profit margin.
Principles of Price Policy
Several principles should be considered while creating a price policy. Generally, new industries accept the generalized policies or policies drafted by renowned economists.
Below are some principles by V.K.R.V Rao which gives precise principles for effective pricing.
Income & Production equality
Income, output, and employment are directly related to each other at the macro level. Increased production leads to a rise in outputs. This leads to a rise in the employment of new entrants.
The government continuously strives for an increase in income that should be equal to an increase in output. This is so because, if the supply of goods is limited and income is increasing then demand would continuously rise. This will lead to inflation in the economy.
Savings and investment equilibrium
Sir Rao also stated that there should be a balance between savings and investment.
If saving is more than investment, the level of demand in the economy shall fall which would further lead to a fall in the price of goods. However, if savings are less than investment then prices ought to rise, as people readily buy products as demand for goods increases.
Buffer Stock
Next important principle that Sir Rao emphasized dealt with buffer stock.
What happens to the stock of umbrellas in winters and stock of jackets in monsoon? They are stored in buffer stocks.
Buffer stock acts as a warehouse and price regulator of these goods. In times of urgency or crisis, buffer stock can release these goods in the market without charging additional prices. Also, at a time of low demand, it can store back these goods in the buffer so that there is no change in their price.
Some other principles like distribution management, income increase by transfer, etc. also play a major role as principles of Price Policy.