Contents
Meaning of Financial Market
The financial market is a market where the trading of various financial instruments occurs, including the stock market, forex market, derivatives market, and other.
In other words, financial market is a place where buyers and sellers are involved in the sale and purchase of financial products like shares, mutual funds, bonds, and so on.
Financial Market is a place where Buying and Selling of shares, bonds, securities etc. take place. A financial market may be a physical location or a virtual one(i.e, Internet).
Prices of securities depend on the demand of the securities, if the demand of the security is high then the price will high if the demand will low then price will also low of the security.
The stock market is a financial market that connects buys and sellers. The financial markets are places where the savings from several sources are mobilized towards investment.
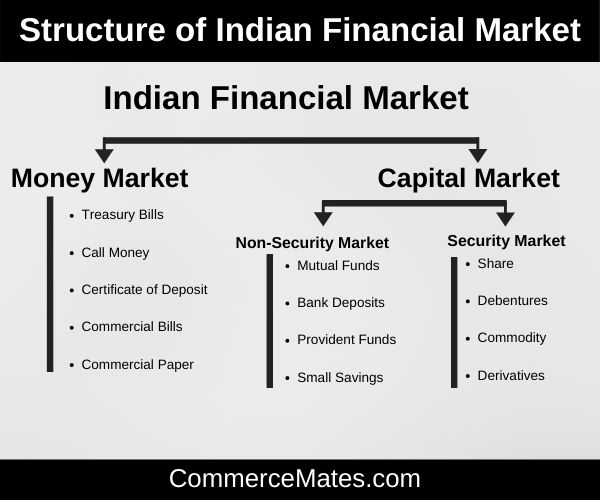
Structure of Indian Financial Market
Indian Financial Market include two market
- Money Market
- Capital Market
Money Market
money market comes under the Financial Market. The money market refers to trading in very short-term debt investments form 1 to 90 days. It is regulated by RBI(reserve bank of India). It is the wholesale market the transaction volume in this market is large.
Instrument trade in Money market are given below:
- Treasury Bills: These are negotiable financial assets. It is issued by the central bank of India. T-bills are issued for 91 days or182 days or 364 days. The interest rate of T-bills is determined by the market forces.
- Call Money: Call money is money borrowed on demand for a very short term. It is issued only for one day. It needs when a sudden demand for funds is required.
- Certificate of Deposit: Certificate of Deposit is a saving certificate with a fixed maturity date. It is an unsecured, negotiable financial instrument. It can issue to institutions, individuals, corporations, trust, and funds. it varies from 7 days to one year.
- Commercial Bills: A commercial or bill of exchange bill arise out of a genuine trade transaction. It is high liquidity and has low risk. it varies from 7 days to one year.
- Commercial Paper: Commercial bills are unsecured, short-term debt issued by a corporation, all-Indian institutions. it varies from 7 days to one year. it can issue to individuals, Banking Company, NRI, and Foreign Institutional investors.
Capital Market
Capital market is a Financial Market where the trade of shares, Debentures, bonds, and other long-term investments take place. It deals with the medium term and long term instruments. It is regulated by the SEBI(Securities and Exchange Board of India)
It is a Capital markets are composed of primary and secondary markets.
- Primary Markets: The market place for new Debentures, bonds, and other long-term investments is called the primary market. In this market prices are fixed.
- Secondary Markets: The place where issued securities are traded is called Secondary Market. In this market prices are determined by the market forces.
Instrument trade in Capital Market are given below:
Non-Security Market
- Mutual Funds: A mutual fund is a combination of securities such as stocks, bonds, and short-term and long term investment. Fund Manager arise money from many investors and invest in lots of financial instruments to minimize the risk.
- Bank Deposits: Bank deposit is the money that you keep in your bank account. It may be in saving account or fixed deposit account.
- Provident Funds: Provident Funds is an investment fund contributed to by employees, employers, In which the full amount with interest is provided to the employee on his/her retirement.
- Small Savings: Saving your earning for your future is called personal savings. We save money for any uncertainty that happens in the future or desire to buy some assets.
Security Market
- Share: Share is the long-term financing source for any company. It is issued to the public and can be traded in the secondary market. The company never takes its share back. There are two types of share, Equity share, and Preference share.
- Debentures: Debentures is a debt instrument issued by the company to the general public to raise the fund for the function of the company. Generally, a debenture is unsecured and it is a long term instrument.
- Commodity: A commodity market is a market where buying, selling, and trading raw or primary products. Example gold, silver and etc.
- Derivatives: A derivative is a financial instrument that is a contract between two people. In derivative, The buyer/seller agrees to purchase/sell the asset on a specific date at a specific price. Types of derivatives are futures/forwards, options, and swaps.