Contents
Meaning of Consumer Decision Making Process
Consumer decision making process involves the consumers to identify their needs, gather information, evaluate alternatives and then make their buying decision.
Consumer Decision-Making Process is one through which a consumer goes through for satisfying their needs by making appropriate buying decisions. It is a complex process which ranges from the recognition of needs, searching and collecting information, evaluating alternatives, purchasing the best product out of alternatives and post-purchase activities.
It is simply a process which depicts the journey of the consumer from starting to end for making buying decisions. Marketers use this process as a source of information for acquiring all important data related to consumers.
Stages of Consumer Decision Making Process
There are several steps involves in decision making process of consumers. These steps are explained in detailed below: –
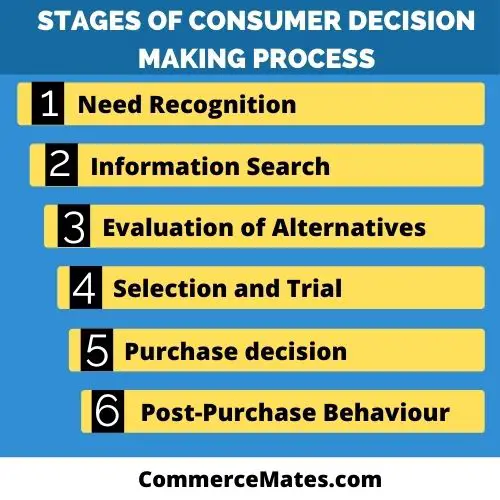
- Need Recognition- Process of consumer decision making starts with the identification of need or problem. It is a stage where consumer found out that they are missing something and look for means for filling such a gap. The consumer determines his wants that motivate him to search for opportunities for satisfaction of his needs.
- Information Search- Once the problem is identified by a consumer, he searches for information regarding distinct products available in the market. Consumer gathers data regarding various products and services that can satisfy his want. He uses both personal as well as a commercial source for this purpose. Personal source involves family, friends, peers etc. and commercial sources involve newspapers, T.V., radio and the internet.
- Evaluation of Alternatives- After gathering information from all sources, consumers checks various product alternatives for selecting the most appropriate one. He evaluates the advantages and disadvantages of different available alternatives. The consumer will develop a set of choices with regard to attributes of product, brand etc. that meet his want, preferences, taste, personality and lifestyle.
- Selection and Trial- Consumer here make his first purchase for the trial of products keeping his set of choices in mind. He purchases several products in small quantities or uses them for a short span of time for developing an opinion towards product.
- Purchase decision- Once the consumer is fully satisfied with the quality of product after taking a trial, he finally buys the product for fulfilling his needs. Here consumer has acquired all of the required knowledge after evaluating all facts and arrive at final conclusion to buy a product. He finally makes a choice of product, brand, dealer, decide an amount and purchase time.
- Post-purchase behaviour- It refers to post-purchase behaviour of consumer where he evaluates whether the product has met his expectations or not. He will find out that a product is either useful or not. There may be three outcomes after making a purchase: – Product actual performance is equal to the expected performance that will lead to repeat purchase decisions by consumers, product actual performance is greater than the expected performance which will lead to build consumer loyalty and third case is where product actual performance is less than expected performance where consumer will reject the product.
Levels of Consumer Decision Making
- Extensive Problem Solving- This is the early stage in decision making of consumer where he has not developed an evaluation criterion. Buyer has a very little information about products and brands, therefore is highly involved with products for their critical evaluation. Large no. of brands is evaluated and there is enough time available for finalizing product. These type of decisions are taken for buying high cost products such as car, bikes etc.
- Limited Problem Solving- Limited problem solving is an advanced stage of consumer’s decision making. Consumer has moderate involvement with products for choosing the suitable one. He conducts a general search for products and only few alternative brands are evaluated. Choice criteria is well defined buyer takes less time to complete purchase process. It takes place in purchasing products like clothes, shoes and cosmetics.
- Routine Response Behaviour- Here, consumers have a very low involvement with products and do a little evaluation of alternatives. He has a strong predisposition towards one brand and takes all purchase decisions frequently. Cost of product purchased is low and any product that fulfil needs is chosen quickly. It applies in case of products like soap, toothpaste, shampoo etc.
Models of Consumer Decision Making
- Economic Model- Economic Model is a model that assumes a consumer to be rational person and all decision are taken by him on rational basis. He has an ability of doing a comparison of variety of products, performing analysis of their advantages and disadvantages which provides them efficient information for taking appropriate purchase decision. He is well-known about all existing alternative brands and give them a ranking considering their features, quality, uses and drawbacks. Economic model is considered to be unrealistic as people do not always behave rationally while purchasing a product and lacks skills, existing values and perceptions.
- Passive Model- Passive model believes that promotional campaigns of marketers influences the decision making process of consumers. They respond directly to advertisement appeal made by brands in market. This model is opposite of economic model, as it believes that evaluation of products will be done by consumer as per their market position and how they are being promoted in the market. Passive model is also an unrealistic model as it ignores the fact that individual have a capability of themselves acquiring information from market for evaluating alternatives before making buying decision.
- Cognitive Model- This one of the best model out of all 4 consumer decision process model. Cognitive model assumes that all purchase decisions are taken by consumer according to their interest and market understandability. This model fully ignores the role of promotional campaigns of marketers and consumer’s rational needs in their decision making process. All marketers must assist consumers in creating short-cut decision rules that would result in fast purchase decisions.
- Emotional Model- Emotional model of consumer decision making assumes that emotions of individual plays a major role in influencing their buying decisions. Consumers are believed to be emotional who acts as per their emotions. They associate themselves with goods and services which results in impulsive decisions by them. Time taken to decide the product is less, and a positive and negative emotion is developed regarding the product. Hence, only those products are purchase that brings positive emotions and all those that brings negative emotions are avoided.
Consumer Decision Rules
- Compensatory Decision Rule- It is a decision rule in which relevant attributes of product are taken into consideration while evaluating them for making a purchase decision. He carefully balances the pros and cons of every attribute of product before finalizing it for purchase.
- Non-compensatory Decision Rule- According to this rule, any positive attribute of product cannot make buyer to overlook its negative attribute. It believes that product positive evaluation will not compensate for negative evaluation of product.
- Conjunctive Decision Rule- Under this rule, a minimum cut-off point is established by consumer for each attribute of product. A brand is avoided if any of its attributes fall below the cut-off point.
- Disjunctive Decision Rule- Here, cut-off point only for relevant attributes of product is established by consumer. Product exceling in at least one attribute is chosen by consumer.
- Lexicographic Rule- It is the one where attributes of product are ranked in terms of their importance and then a comparison of important attributes is done. Product exceling in attributes important to consumer is chosen.